Studies

Effect of Exogenous Ketones as an Adjunct to Low-Calorie Diet on Metabolic Markers
Background/Objectives: Overweight and obesity affect a majority of adults, contribut- ing to metabolic disorders. Caloric restriction often leads to undesirable lean mass loss alongside fat reduction. This study investigated whether exogenous β-hydroxybutyrate (BHB) supplementation, as an adjunct to a hypocaloric diet, improves body composition and metabolic markers in overweight and obese adults by preferentially reducing fat mass while preserving lean mass. Methods: In this 8-week randomized, double-blind, placebo- controlled trial, 51 adults were assigned to receive either racemic BHB mineral salts or placebo (maltodextrin) twice daily, alongside modest caloric restriction. Assessments at baseline and week 8 included dual-energy X-ray absorptiometry for body composition, indirect calorimetry for resting metabolic rate (RMR), and venous blood analyses for car- diometabolic biomarkers (e.g., lipids, HOMA-IR, uric acid, liver enzymes). Results: Body mass decreased in both groups over the intervention (p < 0.01 within placebo and p < 0.001 within BHB). Within the BHB group, fat mass decreased significantly (−2 kg; p < 0.05 vs. baseline), body fat percentage improved (p < 0.01 vs. baseline), and lean-to-fat mass ratio increased (p 0.05). Furthermore, lean mass was largely preserved, with no declines in RMR. Within the BHB group, LDL cholesterol was reduced (p < 0.05 vs. baseline), while other lipids, HOMA-IR, and uric acid remained stable, with liver enzymes showing a positive change. Conclusions: Exogenous BHB supplementation may enhance the quality of diet-induced weight loss through within-group improvements in fat mass reduction and lean mass preservation, with no adverse metabolic impacts.

β-Hydroxybutyrate Reduces Body Weight by Modulating Fatty Acid Oxidation and Beiging in the Subcutaneous Adipose Tissue of DIO Mice
β-hydroxybutyrate (BHB) serves as an alternative cellular fuel during states of low glucose availability, such as fasting or carbohydrate restriction, when the body shifts to using fats and ketone bodies for energy. While BHB has shown potential metabolic benefits, its mechanisms of action in the context of obesity are not fully understood. In this study, we examined the effects of BHB supplementation on subcutaneous adipose tissue (SAT) metabolism in a diet-induced obesity (DIO) mouse model. Adult male mice were first fed a high-fat diet for six weeks, followed by a standard diet with or without BHB supplementation for an additional six weeks. BHB supplementation led to significant body weight loss independent of food intake. This weight reduction was associated with decreased adipocyte differentiation, reflected by reduced peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma (PPARγ) protein levels and lower uncoupling protein 1 (UCP1) expression, indicating altered SAT function. Transcriptomic

Metabolism of Exogenous D-Beta-Hydroxybutyrate, an Energy Substrate Avidly Consumed by the Heart and Kidney
There is growing interest in the metabolism of ketones owing to their reported benefits in neurological and more recently in cardiovascular and renal diseases. As an alternative to a very high fat ketogenic diet, ketones precursors for oral intake are being developed to achieve ketosis without the need for dietary carbohydrate restriction. Here we report that an oral D-beta-hydroxybutyrate (D-BHB) supplement is rapidly absorbed and metabolized in humans and increases blood ketones to millimolar levels. At the same dose, D-BHB is significantly more ketogenic and provides fewer calories than a racemic mixture of BHB or medium chain triglyceride. In a whole body ketone positron emission tomography pilot study, we observed that after D-BHB consumption, the ketone tracer 11C-acetoacetate is rapidly metabolized, mostly by the heart and the kidneys. Beyond brain energy rescue, this opens additional opportunities for therapeutic exploration of D-BHB supplements as a “super fuel” in cardiac and chronic kidney diseases.

Daily Intake of D-B-Hydroxybutyric Acid (D-BHB) Reduces Body Fat in Japanese Adult Participants: A Randomized, Double-Blind, Placebo-Controlled Study
Currently, there is considerable interest in ketone metabolism owing to the benefits for human health. Conventionally, strict dietary restrictions on carbohydrates are required to increase plasma ketone levels, while supplementation with D-ß-hydroxybutyric acid (D-BHB) can easily increase plasma ketone levels. We hypothesized that a daily intake of D-BHB could promote weight loss, especially through fat reduction. Herein, D-BHB (OKETOAT™) was produced via a proprietary fermentation process from sugar. In this ran- domized, double-blind, placebo-controlled study, we assessed the safety and fat-reduction effects after 12 wk of daily ingestion of D-BHB (2.9 g) in 22 healthy Japanese adults and 22 control participants. Blood samples were collected pre- and post-treatment.
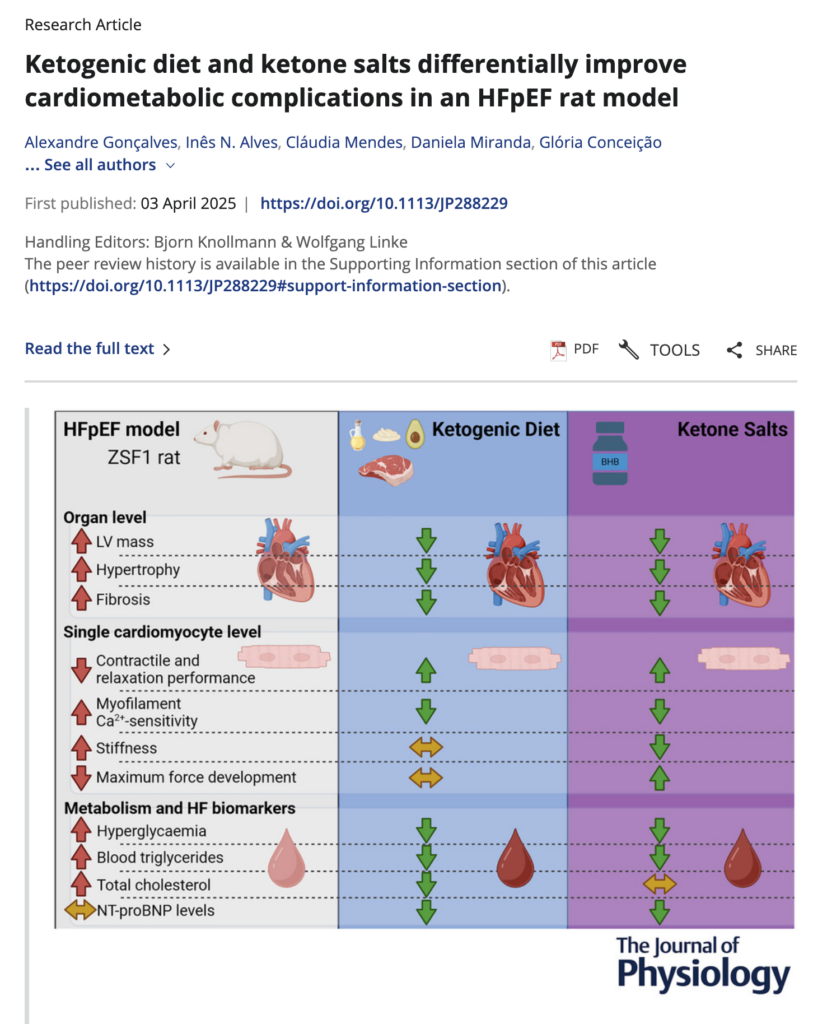
Ketogenic diet and ketone salts differentially improve cardiometabolic complications in an HFpEF rat model
Heart failure with preserved ejection fraction (HFpEF) remains a major health concern with limited therapeutic options. Growing evidence supports the multiple benefits of ketones in heart disease, but their impact on HFpEF remains unknown. We investigated whether increasing ketones can help to manage HFpEF. Using the ZSF1 rat model of HFpEF, 16-week-old rats were randomly assigned to one of three subgroups: (i) control diet; (ii) ketogenic diet (KD); or (iii) control diet with added exogenous ketone salts (KS) in their drinking water for 10 weeks. We found that both KD and KS ameliorated the HFpEF phenotype by improving structural echocardiographic parameters, lowering glycaemia and lipid profiles, and reducing HFpEF-related fibrosis and hypertrophy without impacting in vivo diastolic function. Nevertheless, ex vivo cardiomyocyte preparations showed improved calcium handling and myofilament relaxation, suggesting benefits at the cellular level. Interestingly, KD still proved effective, despite the potentially adverse increase in fat mass.

Effect Of D – Β-Hydr O Xybutyr A Te (should be d – β-hydroxybutyric acid (D-BHB) On Sleep Quality In Healthy Participants: A Randomized, Double-Blind, Placebo-Controlled Study
We investigated the effects of d – β-hydroxybutyric acid (D-BHB) on sleep quality in healthy Japanese adults. In this randomized, placebo-contr olled, doub le-b lind, parallel-gr oup study, each group comprised 30 healthy Japanese adults. Participants received 1.5 g of D-BHB (low D-BHB group), 2.9 g of D-BHB (high D-BHB group), or a placebo beverage (placebo group) for 14 days. Before and after the intervention, the Oguri–Shirakawa–Azumi sleep inventory, middle-aged and aged version (OSA-MA), and sleep state test were conducted. After 14 days, compared to the placebo group, the OSA-MA scores for “Sleepiness on rising” and “Frequent dreaming” wer e significantl y higher in both the low and high D-BHB gr oups. Additionall y, the scor e for “Initiation and maintenance of slee p”w as significantly higher in the low D-BHB group, and the score for “Refreshing on rising”was significantly higher in the high D-BHB group. We found that D-BHB can impr ov e slee p quality in healthy J apanese adults.

